Human prostatic tissue (control / BPH patients)
Human prostatic tissues advantages
- In vitro investigation of human prostate function in normal or in pathophysiological conditions.
- Useful to investigate the effect of drugs developed to improve the dynamic component of prostatic lower urinary tract symptoms associated with benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).
-
Evaluation of the ability of drugs at modulating prostatic smooth muscle tone can be performed
- on adrenergic contractile response elicited by a-adrenergic pharmacological stimulation (phenylephrine/norepinephrine) or by electrical field stimulation (EFS) which stimulates efferent nerve terminals present in the tissue
- on KCl response
- on others relevant physiological precontracted states (endothelin-1, thromboxane agonistů)
- Evaluation of mRNA by RT-PCR or protein expression, by immunohistochemistry (IHC) or western-blot (WB), in parallel of organ bath studies.
Source of human tissues sample
- Human normal prostate samples are obtained from patients undergoing cystoprostatectomy for infiltrating bladder cancer.
- Human BPH samples are obtained from patients diagnosed clinically for BPH and undergoing adenomectomy.
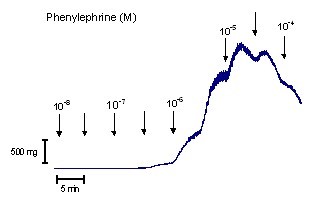
| Figure 1: Original tracing showing the effect of cumulative addition of increasing concentrations of phenylephrine (M) on human prostatic tissue from BPH patient. (Pelvipharm, internal data) |
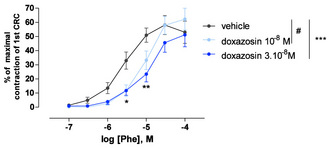 |
| Figure 2: Effect of doxazosin on phenylephrine-induced contractions on human prostatic tissue from control patient. From Oger, S. et al. J Sex Med (2009) : 6(3) : 836-847. |
Endpoints
- Evaluation of the capacity of a drug to inhibit prostatic smooth muscle contractions.
- Determination of potency (EC50) and efficiency (Emax) of a drug.
- Determination of the affinity (pA2) of a drug for a human prostatic receptor.
Related Pelvipharm bibliography
Oger, S. et al.
Eur Urol (2010) : 57(4):699-707
Oger, S. et al.
J Sex Med (2009) : 6(3):836-847
Giuliano, F. et al.
J Urol (2009) : 181(4):693 (AUA, 2009)
Eur Urol (2010) : 57(4):699-707
Oger, S. et al.
J Sex Med (2009) : 6(3):836-847
Giuliano, F. et al.
J Urol (2009) : 181(4):693 (AUA, 2009)

Links to applicable Experimental skills




















 Download this page in PDF
Download this page in PDF