Cyclophosphamide-induced bladder irritation
Modelís advantages
- Cyclophosphamide is a pro drug chemotherapeutic agent which ultimately leads to the formation of acrolein.
- Acrolein damages the bladder urothelium and can lead to hemorrhagic cystitis. Moreover, it produces a marked bladder overactivity mediated through the stimulation of C-fiber afferent.
- Useful to evaluate the effect of a drug on bladder inflammatory processes such as interstitial cystitis.
Species
Rat
pHYSIOLOGICAL FEATURES
- Abnormal bladder function; cystometrogram displays a decrease in intercontraction interval and a decrease in bladder capacity.
- Hematuria.
- Bladder wall edema.
- Increase in bladder weight.
- inflammatory cell (polymorphonuclear neutrophils) infiltration in the bladder lamina propria.
- Increase C-Fos positive cells in the spinal cord (L6 level).
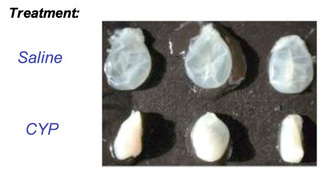 |
| Figure 1: Representative pictures illustrating the inflammatory effect of cyclophosphamide on bladders from cyclophosphamide (CYP) treated rats. (From Giuliano.f et al. 2006). |
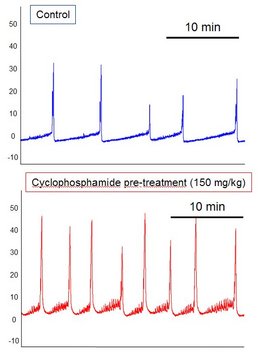 |
| Figure 2 : Representative cystometrograms in anesthetized rats showing the effect of cyclophosphamide pre-treatment. (PVP, internal data). |
Summarized methodology
Rats are injected with vehicle or cyclophosphamide intraperitoneally (i.p) at the dosing of 100 mg/kg 48h before testing. Thereafter, urodynamic evaluation can then be performed (cf. Links to applicable experimental skills)
Related Pelvipharm bibliography
Giuliano, F. et al.
Brit J Urol (2006) : 97(2):386-392
Brit J Urol (2006) : 97(2):386-392

Links to applicable Experimental skills




















 Download this page in PDF
Download this page in PDF