Spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR)
Model advantages
This rat model is the most widely used animal model of hypertension and develops many features of human hypertensive end-organ damage such as cardiac hypertrophy, cardiac failure and renal dysfunction.
Pathophysiological features
Cardiovascular features :
- Spontaneous severe hypertension with blood pressure stabilization around 12 weeks of age (>160 mmHg).
- Differential sensitivity to various hypertensive agents (figure 1)
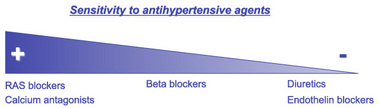 |
| Figure 1: Blood pressure-lowering efficacy of common antihypertensive agents in SHR. |
- Endothelial dysfunction
- Vascular remodeling
- Cardiac hypertrophy
- Exhibits some features of metabolic syndrome: insulin resistance, hyperinsulinemia, hypertriglyceridemia, hypertension
- Sympathetic hyperactivity
Erectile function features:
- Erectile dysfunction preceding the elevation of blood pressure (figure 2).
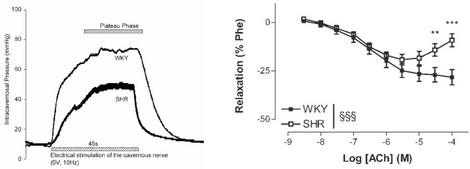 |
| Figure 2: In vivo (left panel) and in vitro (right panel) evidence of erectile dysfunction in 12 week-old SHR. From Behr-Roussel et. Al, 2005 |
- Corpora cavernosa remodeling
- Cavernosal endothelial dysfunction
Bladder function features
- Changes in neuronal morphology (increase in bladder afferents) and function similar to those that occur with obstruction of the bladder outlet as it is the case in patients with lower urinary tract symptoms associated with benign prostatic hyperplasia
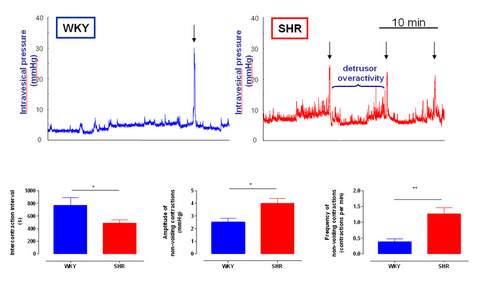
- Exhibits abnormal bladder function: decreased bladder capacity and voided volume, increased urinary frequency, and occurrence of non voiding contractions associated with changes in the noradrenergic control of the micturition reflex.
- Increase in α-adrenoceptor agonist responsiveness of detrusor strips in vitro in organ baths
- Increase in urethral α-adrenoceptor agonist responsiveness in vitro in organ baths
Related Pelvipharm bibliography
Behr-Roussel, D. et al.
Am J Physiol - Regul (2005) : 288:R276-R283
Behr-Roussel, D. et al.
Am J Physiol – Regul (2003) : 284:R682-R688
Am J Physiol - Regul (2005) : 288:R276-R283
Behr-Roussel, D. et al.
Am J Physiol – Regul (2003) : 284:R682-R688

Links to applicable Experimental skills
- Administration routes / Regimen
- Behavioural Science
- Confocal Microscopy
- Erection elicited by pharmacological or electrical neural stimulation
- Immunohistology
- Ischemia / Reperfusion Injury
- Metabolic cages (diuresis, renal function, spontaneous micturition)
- Morphology
- Morphometry
- Non invasive blood pressure monitoring (tail cuff)
- Organ bath with animal tissues (In Vitro studies)
- Oxidative fluorescence
- Plasma / urine / tissue collection
- Protein expression and activity
- Spectrophotometric assays
- Telemetry
- Urodynamic evaluation (anesthetized)
- Urodynamic evaluation (conscious)




















 Download this page in PDF
Download this page in PDF