Testosterone-supplemented SHR as a model of BPH / male LUTS
Model advantages
The testosterone-supplemented SHR combines erectile dysfunction, prostate enlargement and urodynamic impairment characteristic of LUTS and allows thus the assessment of erectile function in parallel to bladder function and prostate size.
This model helps to assess the sexual side-effect profile of new therapeutic strategies for BPH while evaluating their efficacy on LUTS and prostate enlargement.
Pathophysiological features
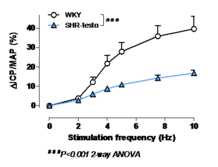
Erectile dysfunction:
- Dramatic impairment of erectile responses to electrical stimulation of the cavernous nerve after 3 weeks of testosterone supplementation in anesthetized SHR (figure 1).
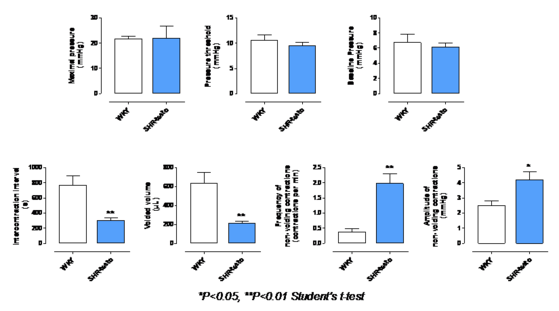
Bladder dysfunction
- Exhibits abnormal bladder function: decreased ICI, voided volume and bladder capacity, and increased urinary frequency and amplitude of non voiding contractions characteristic of detrusor overactivity.
 Prostate enlargement
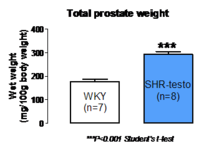
Prostate enlargement
The testosterone-supplemented SHR exhibits several common characteristics with the human pathology:
- Prostatic enlargement (figure 3)
Related Pelvipharm bibliography
Oudot A., et al.
J Urol (2011) : 185, 4, Suppl 1, p.e631
Oudot A., et al.
J Sex Med (2010) : 7(s6)
J Urol (2011) : 185, 4, Suppl 1, p.e631
Oudot A., et al.
J Sex Med (2010) : 7(s6)

Links to applicable Experimental skills
- Confocal Microscopy
- Ejaculation
- Ejaculation elicited by pharmacological or electrical neural stimulation
- Erection elicited by pharmacological or electrical neural stimulation
- Immunohistology
- Metabolic cages (diuresis, renal function, spontaneous micturition)
- Morphology
- Morphometry
- Non invasive blood pressure monitoring (tail cuff)
- Organ bath with animal tissues (In Vitro studies)
- Oxidative fluorescence
- Protein expression and activity
- Spectrophotometric assays
- Telemetry
- Urodynamic evaluation (anesthetized)
- Urodynamic evaluation (conscious)




















 Download this page in PDF
Download this page in PDF