Rat model of cavernous nerve crush injury
Model advantages
This rat model of cavernous nerve crush injury mimics neural damages associated with radical prostatectomy in human.
Pathophysiological features
Identically to human, the rat model of cavernous nerve crush injury displays ED (figure 1).
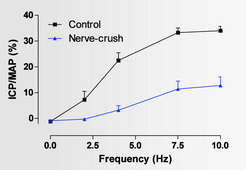 |
| Figure 1: Effects of bilateral cavernous nerve crush injury (4 weeks post-surgery) on intracavernosal pressure (ICP) after ES CN in anesthetized rats (from Bessede T et al., 2008). |
Moreover, several pathophysiological mechanisms which are linked to radical prostatectomy-associated ED in human are present in rats with cavernous nerve crush injury:
- Penile nNOS immunoreactive fibers content decrease. (The brief activation of nNOS is involved in the initiation of the erectile process causing the increase in intracavernosal pressure)
- Cavernosal tissue remodeling and fibrosis
Summarized methodology
Briefly, bilateral cavernous nerve crush is performed in rats under anaesthesia usually 3-4 weeks before experimentation (figure 2).
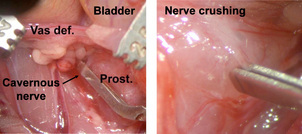 |
| Figure 2: Per-operative view of cavernous nerve crush procedure in rats. |
Related Pelvipharm bibliography
Oudot, A. et al.
Eur Urol (2011) : 60(5):1020-1026
Bessede, T. et al.
J Sex Med (2008) : 5 (suppl 2) (ESSM 2008)
Bessede, T. et al.
Eur Urol Suppl : 7(3):161 (EAU 2008)
Eur Urol (2011) : 60(5):1020-1026
Bessede, T. et al.
J Sex Med (2008) : 5 (suppl 2) (ESSM 2008)
Bessede, T. et al.
Eur Urol Suppl : 7(3):161 (EAU 2008)

Links to applicable Experimental skills
- Administration routes / Regimen
- Behavioural Science
- Confocal Microscopy
- Erection elicited by pharmacological or electrical neural stimulation
- Immunohistology
- Metabolic cages (diuresis, renal function, spontaneous micturition)
- Morphology
- Morphometry
- Organ bath with animal tissues (In Vitro studies)
- Oxidative fluorescence
- Plasma / urine / tissue collection
- Protein expression and activity
- Spectrophotometric assays
- Telemetry




















 Download this page in PDF
Download this page in PDF