Spinal cord injury-induced neurogenic detrusor overactivity
Modelís advantageS
- The most commonly utilised and highly informative model of a central lesion with respect to lower urinary tract function
- used for the evaluation of drugs targeting neurogenic detrusor overactivity (NDO) but also overactive bladder whatever its etiology
- useful to investigate the effect of mechanisms known to act on C-fiber afferents
- useful to investigate an effect on the external urethral sphincter activity
SPECIES
rat
Pathophysiological featureS
- Mimics the voiding patterns of patients with neurogenic detrusor overactivity due to spinal cord injury
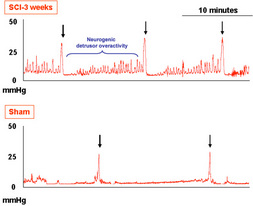
- Display neurogenic detrusor overactivity characterized by non-voiding contractions during the filling phase with increased maximal micturition pressure and increased micturition duration.
- Reduced voiding efficiency and large residual urine volume associated with detrusor-sphincter dyssynergia
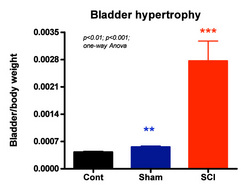
- Bladder hypertrophy
- Increase in bladder afferent nerve activity, in particular through C-fibers
- BBB score impairment altered locomotor activity (reduced BBB score)
 |
Summarized methodology
A T7-T8 laminectomy is performed and the spinal cord is cut between T7 and T8 vertebrae. A sterile gelform sponge is placed between the cut ends of the spinal cord.
Neurogenic detrusor overactivity progressively develops over time until 3-4 weeks where it is stabilized.
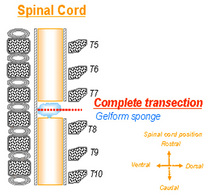 |
| Figure 2: Complete transection between vertebral T7-T8. |
Related Pelvipharm bibliography
Broqueres-You, D. et al. Basic & Clinical Pharmacology & Toxicology, 107 (Suppl. 1), 192 (WorldPharma 2010)
Behr-Roussel, D. et al. J Urol (2010) : 183(4),supl1:e391 (AUA, 2010)
Broqueres-You, D. et al. J Urol (2010) : 183(4),supl1:e76-e77 (AUA, 2010)
Behr-Roussel, D. et al. Eur Urol Suppl (2010) : 9(2):73 (EAU, 2010)
Broqueres-You, D. et al. Eur Urol Suppl (2010) : 9(2):112 (EAU, 2010)
Broqueres-You, D. et al. Neurourol Urodyn (2009) : 28(7):695 (ICS, 2009)
Broqueres-You, D. et al. J Urol Abstract (AUA, 2008) : 179(4) : 348-349
Behr-Roussel, D. et al. J Urol (2010) : 183(4),supl1:e391 (AUA, 2010)
Broqueres-You, D. et al. J Urol (2010) : 183(4),supl1:e76-e77 (AUA, 2010)
Behr-Roussel, D. et al. Eur Urol Suppl (2010) : 9(2):73 (EAU, 2010)
Broqueres-You, D. et al. Eur Urol Suppl (2010) : 9(2):112 (EAU, 2010)
Broqueres-You, D. et al. Neurourol Urodyn (2009) : 28(7):695 (ICS, 2009)
Broqueres-You, D. et al. J Urol Abstract (AUA, 2008) : 179(4) : 348-349

Links to applicable Experimental skills
- Administration routes / Regimen
- Bladder blood flow
- Confocal Microscopy
- Electrophysiology
- Eye Wipe Test
- Immunohistology
- Locomotor activity evaluation
- Metabolic cages (diuresis, renal function, spontaneous micturition)
- Morphology
- Morphometry
- Neural firing recording
- Neuro-anatomical tracing techniques
- Organ bath with animal tissues (In Vitro studies)
- Oxidative fluorescence
- Plasma / urine / tissue collection
- Protein expression and activity
- Spectrophotometric assays
- Urodynamic evaluation (conscious)




















 Download this page in PDF
Download this page in PDF