Bladder outlet obstruction (BOO)
Model’s advantages
- shows many of the morphological and functional changes as those seen in patients with severe bladder outlet obstruction
- allows changes to develop overtime as the animal grows and becomes progressively more obstructed
- useful to investigate the effect of drugs known to act on both bladder smooth muscle and afferent responses
SPECIES
rat, rabbit
Pathophysiological features
- Morphological changes: smooth muscle hyperplasia and hypertrophy
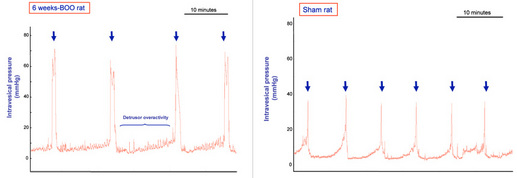
- Functional changes: increased bladder capacity, residual volume, and micturition pressure in addition to the occurrence of detrusor overactivity characterized by non-voiding contractions
Summarized methodology
A calibrated gold jeweler’s jump ring, is twisted open and passed around the proximal urethra. It is freely mobile around the urethra; thus, as the animal grows, progressive bladder outlet obstruction develops. The pathology develops 4-6 weeks after BOO. Urodynamic evaluation can then be performed (cf. Links to applicable experimental skills).
NB: Pelvipham will gladly study the feasibility to fit this experimental model in order to meet its client’s needs.
Related Pelvipharm bibliography
Oger, S. et al.
Eur Urol Suppl (2007) : 6(2):102 (EAU, 2007)
Oger, S. et al.
J Urol (2007) : 177(4) (AUA, 2007)
Julia-Guilloteau, V. et al.
Eur Urol (2006) : 5(2):78 (EAU, 2006)
Eur Urol Suppl (2007) : 6(2):102 (EAU, 2007)
Oger, S. et al.
J Urol (2007) : 177(4) (AUA, 2007)
Julia-Guilloteau, V. et al.
Eur Urol (2006) : 5(2):78 (EAU, 2006)

Links to applicable Experimental skills
- Administration routes / Regimen
- Bladder blood flow
- Confocal Microscopy
- Immunohistology
- Metabolic cages (diuresis, renal function, spontaneous micturition)
- Morphology
- Morphometry
- Neural firing recording
- Organ bath with animal tissues (In Vitro studies)
- Oxidative fluorescence
- Plasma / urine / tissue collection
- Protein expression and activity
- Spectrophotometric assays
- Urodynamic evaluation (anesthetized)
- Urodynamic evaluation (conscious)




















 Download this page in PDF
Download this page in PDF