Capsaicin-induced bladder hyperactivity
Model’s advantages
- Capsaicin is a selective excitotoxin of C-fiber primary afferent neurons.
- Acts through the stimulation of a vanilloid receptor (VR1).
- Release of tachykinins and other mediators at both the peripheral and spinal cord level.
- Useful for quick investigation of the effect of drugs known to act on C-fiber afferents.
SPECIES
rat, guinea pig
Pathophysiological features
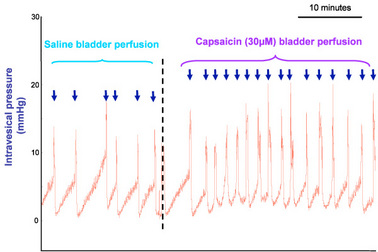
- Cystometrogram displays:
- decrease in the intercontraction interval.
- decrease in the pressure threshold for eliciting contractions.
- Increase C-Fos positive cells in the spinal cord (L6 level).
Summarized methodology
The bladder is perfused with continuous capsaicin (30 µM) at a rate of 50 µl/min while intravesical and blood pressure are monitored concomitantly.
NB: Pelvipham will gladly study the feasibility to fit this experimental model in order to meet its client’s needs.
Related Pelvipharm bibliography
Caremel, R. et al. Eur Urol (2010) : 58(4):616-25

Links to applicable Experimental skills




















 Download this page in PDF
Download this page in PDF