Fructose fed rats (FFR)
Model advantages
The development of metabolic abnormalities induced by a fructose-enriched diet in rats is similar to what is observed in humans following an increased consumption of high-fructose corn sweetener (HFCS). Indeed, these HCFS is likely a decisive contributing factor to the development of obesity and the accompanying metabolic abnormalities observed in the insulin resistance syndrome.
Pathophysiological features
Metabolic features :
- Hypertriglyceridemia
- Hypercholesterolemia
- Hyperinsulinemia
- Insulin resistance and exaggerated hyperglycaemic response to glucose overload
- Elevated urinary 8-isoprostanes (lipid peroxidation)
Cardiovascular features:
- Vascular endothelial dysfunction (aorta and superior mesenteric artery) (figure 1)
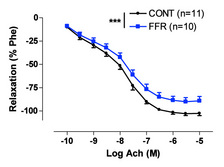 |
| Figure 1: Comparison of endothelium-dependent relaxations obtained in in vitro experiments performed in aortic rings. (2-way ANOVA, ***P<0.001) (From Oudot et. al. 2008). |
- Exaggerated blood pressor response in vivo in conscious unrestrained animals (figure 2)
Summarized methodology
Wistar rats are placed on a control or an isocaloric fructose-enriched diet containing 60% fructose and 5.2% lard for the following 9 weeks to allow the metabolic abnormalities to develop.
Related Pelvipharm bibliography
Oudot, A. et al.
J Sex Med (2010) : 7(1)p1:79-88
Oudot, A. et al.
Physiol Res (2009) : 58(4):499-509
Behr-Roussel, D. et al.
Eur Urol (2008) : 53(6):1272-1281
Behr-Roussel, D. et al.
Am J Hypertens (2008) : 21(11):1258-1263
J Sex Med (2010) : 7(1)p1:79-88
Oudot, A. et al.
Physiol Res (2009) : 58(4):499-509
Behr-Roussel, D. et al.
Eur Urol (2008) : 53(6):1272-1281
Behr-Roussel, D. et al.
Am J Hypertens (2008) : 21(11):1258-1263

Links to applicable Experimental skills
- Administration routes / Regimen
- Confocal Microscopy
- Immunohistology
- Metabolic cages (diuresis, renal function, spontaneous micturition)
- Morphology
- Morphometry
- Non invasive blood pressure monitoring (tail cuff)
- Organ bath with animal tissues (In Vitro studies)
- Oxidative fluorescence
- Plasma / urine / tissue collection
- Protein expression and activity
- Spectrophotometric assays
- Telemetry




















![Figure 2: Concentration response curves to increasing doses of norepinephrine infusion (0 to 400 ng/kg/min) on mean arterial pressure (MAP) measured in vivo in conscious animals [control and fructose-fed rats (FFR)] (From Oudot et al. J Physiol Res 2008).](http://www.pelvipharm.com/photos/services/art_14/B_Met_AO_2_2.jpg)
 Download this page in PDF
Download this page in PDF