Urethral pressure and EUS-EMG measurements
Objectives
- measuring intraurethral pressure
- measuring the external urethral sphincter activity by electromyogram (EUS-EMG)
- performed in anaesthetised animals in either normal or pathophysiological animal models
- useful to investigate the effect of a drug for pathology associated with alteration of urethral function such as lower urinary tract symptoms / benign prostatic hyperplasia, neurogenic detrusor overactivity associated with detrusor sphincter dyssynergia and mixed or stress urinary incontinence
- useful to investigate the effect of a drug targeting ejaculatory dysfunctions such as premature ejaculation, anejaculation or retrograde ejaculation
- the measurement of urethral, EUS-EMG and vesical pressures can be performed simultaneously in order to assess the coordination between the detrusor and the sphincter
Species
rat, guinea pig
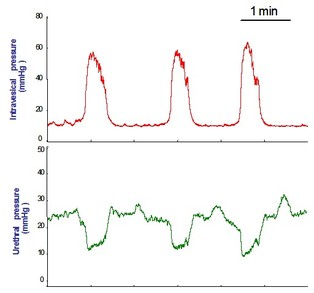 |
| Fig 1: Representative recording of intravesical pressure and urethral pressure during reflex bladder contractions in urethane anesthetized female rat. |
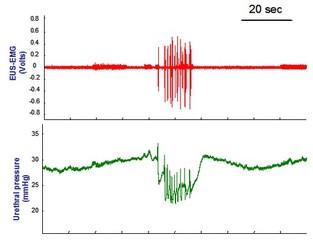 |
| Fig 2: Representative recording of urethral pressure and EUS-EMG during an ejaculatory response induced by systemic p-chloroamphetamine in urethane anesthetized male rat. |
Summarized methodology
Two catheters are inserted via the bladder dome. One allows the measurement of intravesical pressure and the perfusion of the bladder (50 µl/min) (isovolumetric cysometry); the other is inserted into the proximal urethra and allows the measurement of urethral pressure and urethral perfusion (75 µl/min). For experiments in female rats, the separation of the bladder and urethral lumen is performed by a ligature of the urethra by placing a tie just distal to the bladder neck.
For EUS-EMG measurement, electromyogram electrodes are placed into the periurethral striated muscle.
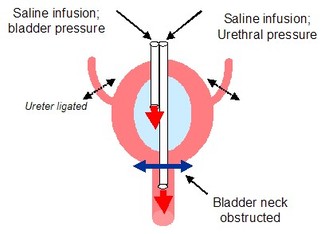 |
| Fig 3: Schematic representation of the experimental method used for measuring both bladder and urethral pressure. |
Endpoints
Urethral function
- Frequency of urethral relaxation
- Amplitude of urethral relaxation
EUS activity
- Amplitude (µvolts) and frequency of bursts
- Duration of the bursting period
Bladder function
- Frequency of bladder contractions (indicator for afferent function of the micturition reflex)
- Amplitude of bladder contraction (indicator for smooth muscle function)
NB: Pelvipharm will gladly study the feasibility of evaluating urethral pressure and EUS-EMG measurement experiments in other experimental models to meet its client’s need.

Links to applicable Targeted disorders / Pathophysiological models




















 Download this page in PDF
Download this page in PDF