Erection induced by the dopamine agonist apomorphine
Objective
To induce erection and record intracavernous pressure (ICP) as a physiological marker of the erectile function. This model can be used in anaesthetised or conscious male rats for testing possible deleterious effects of drugs on erection.
Summarized methodology
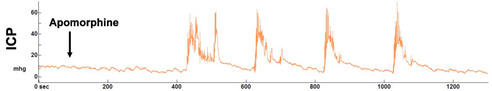
Anaesthetised animals: After anaesthesia induction with urethane, carotid artery and corpus cavernosum are catheterised for arterial pressure and ICP measurements respectively. After an ICP baseline is obtained, apomorphine, is injected subcutaneously at a dose of 200 µg/kg and ICP is recorded for 30 minutes (figure 1). Analysis of the ICP recording is performed a posteriori using custom-written routines in Elphy software (Sadoc, CNRS, Gif-sur-Yvette, France).
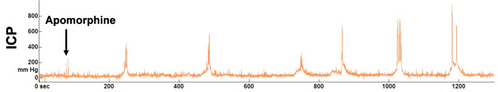
Conscious animals: The telemetric device (model TA11PA-C40, Data Sciences International; figure 1) is implanted to rats under isoflurane anaesthesia. The tip of the catheter is inserted into the proximal shaft of the corpus cavernosum for ICP measurement. The other end of the catheter is connected to the core of the pressure transmitter positioned laterally under the skin of the abdominal wall. After one-week post-surgical recovery period, rats are placed in the experimental setting equipped with a radiofrequency signal receiver that forwards telemetric signal to a computer (figure 2). After an ICP baseline is obtained, apomorphine, is injected subcutaneously at a dose of 80 µg/kg and ICP is recorded for 30 minutes (figure 2). Analysis of the ICP recording is performed a posteriori using custom-written routines in Elphy software (Sadoc, CNRS, Gif-sur-Yvette, France).
Endpoints
- Number and latency of erectile events (corresponding to ICP increases higher than ICP baseline + 3 standard deviations)
- Amplitude of ICP increases
- Duration of ICP increases
- Area under the curve of ICP increases
| Figure 1: Example of intracavernous pressure (ICP) continuous recording in anaesthetised rat administrated with subcutaneous apomorphine 200µg/kg (Pelvipharm internal data). |
| Figure 2: Example of intracavernous pressure (ICP) continuous telemetric recording in conscious, freely moving rat administrated with subcutaneous apomorphine 80µg/kg (Pelvipharm internal data). |
Am J Physiol (1999) : 276:R441-449





















 Download this page in PDF
Download this page in PDF