Erectile function evaluation by electrical stimulation of the cavernous nerve in anesthetized animals (rat-mouse-rabbit)
Objectives
Electrical stimulation of the cavernous nerve (ES CN) in anesthetized animals aims at evaluating the extent of an erectile dysfunction but also the beneficial pro-erectile facilitator effect of a substance administered either chronically or acutely.
Summarized methodology
Erectile responses are elicited by ES CN and measured by monitoring intracavernous pressure (ICP) in anesthetized animals as described in figure 1. The carotid artery and corpus cavernosum are catheterized to record blood pressure (BP) and ICP respectively. A bipolar platinum electrode connected to an electrical stimulator is place on the CN to allow ES at different stimulation frequencies in view of establishing a frequency-response curve (figure 2).
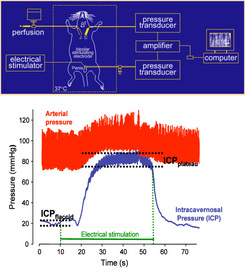 |
| Figure 1: Schematic view of the experimental setting and typical recording of intracavernosal pressure (ICP) and blood pressure during an electrical stimulation of the cavernous nerve. |
 |
|
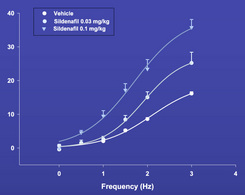
Figure 2: Effects of acute sildenafil intravenous injection (0.03 or 0.1 mg/kg i.v.) on intracavernosal pressure (ICP) after ES CN in anesthetized rats |
Endpoints
- Mean arterial pressure (MAP)
- ΔICP (mmHg) / MAP (mmHg) x 100 with ΔICP being the difference between ICP (intracavernosal pressure in the flaccid state, i.e. before stimulation and ICP during the plateau phase of the erectile response,
- AUC / MAP with AUC, the area under the curve during the erectile response, measured from the beginning of the electrical stimulation until the end of the erectile response and determined using the ICP level in the flaccid state before the onset of the stimulation.
ICP increase and AUC are normalized with MAP to account for the close influence of the systemic blood pressure in the amplitude of ICP increase during the plateau phase of the erectile response.
in Sexual Medicine in Standard Practice in Sexual Medicine (2006) : 1-17
Behr-Roussel, D. et al.
J Sex Med (2006) : 3(4):596-603
Giuliano, F. et al.
Neuroscience (2006):138(1):293-301
Behr-Roussel, D. et al.
Eur Urol (2005) : 47(1):87-91
Behr-Roussel, D. et al.
Am J Physiol – Regul (2005) : 288:R276-R283
Giuliano, F. et al.
Physiol Behav (2004) : 83:189–201
Behr-Roussel, D. et al.
Am J Physiol – Regul (2003) : 284:R682-R688
Giuliano, F. et al.
Eur Urol (2003) : 44(6):731-736
Behr-Roussel, D. et al.
Atherosclerosis (2002) : 162:355-362
Giuliano, F. et al.
J Impot Res (2001) : 13:1-3
Sironi, G. et al.
J Pharm Exp Ther (2000) : 292(3):974-981
Giuliano, F. et al.
in Textbook of Erectile Dysfunction (1999):43-50
Giuliano, F. et al.
Urol Clin North Am (1995) : 22:747-765
Bernabé, J. et al.
Physiol Behav (1995) : 5:837-841
Giuliano, F. et al.
J Auton Nerv Syst (1995) : 55:36-44
Giuliano, F. et al.
J Urol (1993) : 150:519-524

Links to applicable Targeted disorders / Pathophysiological models




















 Download this page in PDF
Download this page in PDF